PROGRAMS
FITNESS & NUTRITION PROGRAMS
Fitness & Nutrition Programs
FITNESS & NUTRITION PROGRAMS
Fitness & Nutrition Programs
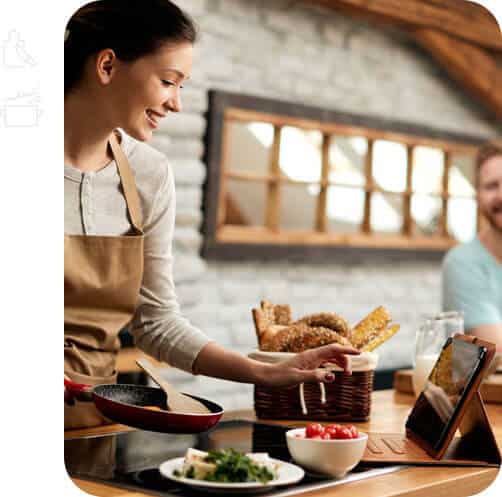
2-on-1 Coaching1-on-1 NutritionSCIENCE BACKED PRODUCTS
Thoroughly researched and scientifically sound products to help hit your goals.
ABOUT
Menu















 1170 Calories
1170 Calories
 217 Calories
217 Calories